elevated lv filling pressure meaning | impaired Lv relaxation on echo elevated lv filling pressure meaning Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) plays a key role in the pathophysiology of heart failure (HF). It is caused by impaired left ventricular (LV) relaxation with or without reduced restoring forces and increased Lv chamber stiffness leading to the inability of the ventricle to fill adequately . See more Growatt MAX 125 KTL3 LV | 3-Phase industrial inverter. Growatt MAX TL3-X LV is energy storage three-phase inverter designed for residential and comercial applications. Available capacities: 50kW, 60kW, 70kW, 80kW, 100kW, 110kW, 120kW, 125kW.
0 · lvedp blood pressure chart
1 · left ventricular pressure chart
2 · left ventricular diastolic dysfunction symptoms
3 · increased left ventricular filling pressure
4 · impaired Lv relaxation on echo
5 · elevated left ventricular filling pressures
6 · elevated left sided filling pressures
7 · Lv filling pressure normal range
Level: 160; HP: 3,760,000,000; MP: 60,000; PDR: 40%; MDR: 40%; EXP: 8,877,840; A stronger version of Livyatan, which comes in blue. It appears during trade voyages from Commerci to Lith Harbor. It can breathe water at you, with super knock back. It can also cause water to rise from the ocean, which renders it invincible due to a glitch.
lvedp blood pressure chart
Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) plays a key role in the pathophysiology of heart failure (HF). It is caused by impaired left ventricular (LV) relaxation with or without reduced restoring forces and increased Lv chamber stiffness leading to the inability of the ventricle to fill adequately . See moreLeft ventricular filling pressure is the pressure that fills the ventricle in diastole and determines stroke volume according to the Frank-Starling mechanism. In patients with HF, . See moreIdentification of elevated LVFP at rest or during exercise is pivotal for the diagnosis of HFpEF, which gained additional interest since medical . See more
A number of echocardiographic parameters may be used to differentiate between normal and elevated LVFP. All the recommended . See more
Figure 1 shows the algorithm recommended by the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) to evaluate LVFP.2 Importantly, the recommendations advocate careful consideration of all available clinical, 2D, and Doppler data to . See more
Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation. Left ventricular filling pressure is the pressure that fills the ventricle in diastole and determines stroke volume according to the Frank-Starling mechanism. In patients with HF, there is typically elevated LVFP at rest, and in some cases only during exercise. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation.
Left ventricular hypertrophy is a thickening of the wall of the heart's main pumping chamber, called the left ventricle. This thickening may increase pressure within the heart. The condition can make it harder for the heart to pump blood. The most common cause is .
Patients with elevated LV filling pressures are at increased risk of death, irrespective of myocardial ischemia or LV systolic dysfunction. These findings support the routine incorporation of LV filling pressure assessment, both before and immediately following stress, into the evaluation of patients referred for exercise echocardiography.Diastolic dysfunction may occur when your ventricles are stiff and don’t relax properly. When this happens, your ventricles don’t fill with blood as they should, and you may experience pressure buildup in your heart. This can progress to diastolic heart failure, resulting in fluid buildup in your lungs, abdomen and legs.
Results: Mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 47%, with 209 patients having an LVEF <50%. Invasive measurements showed elevated LV filling pressure in 58% of patients.For patients with normal LV ejection fraction, normal LV filling pressure is present if E/e′ is less than 8. If septal E/e′ is 15 or more, lateral E/e′ is 12 or more, or average E/e′ is 13 or more, elevated LV filling pressure is present.Despite the presence of impaired left ventricular relaxation, the markedly elevated left atrial pressure results in a high velocity of early diastolic filling, which stops abruptly because of an abnormally rapid rise in ventricular pressure and atrial dysfunction.As LV filling pressure progressively elevate, the LAVI size will enlarge. Therefore, an enlarged LAVI is a marker of elevated LAP. In contrast, a small or normal LAVI is suggestive of normal LAP. The abnormal cut-off value for LAVI is > 34mL/m².
An elevated left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) localizes pathology to the level of the left ventricle and provides a measure of preload, but it is important to recognize that the LVEDP and LA pressure provide complementary, but not interchangeable, information. Left ventricular filling pressure is the pressure that fills the ventricle in diastole and determines stroke volume according to the Frank-Starling mechanism. In patients with HF, there is typically elevated LVFP at rest, and in some cases only during exercise.

left ventricular pressure chart
Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation. Left ventricular hypertrophy is a thickening of the wall of the heart's main pumping chamber, called the left ventricle. This thickening may increase pressure within the heart. The condition can make it harder for the heart to pump blood. The most common cause is . Patients with elevated LV filling pressures are at increased risk of death, irrespective of myocardial ischemia or LV systolic dysfunction. These findings support the routine incorporation of LV filling pressure assessment, both before and immediately following stress, into the evaluation of patients referred for exercise echocardiography.Diastolic dysfunction may occur when your ventricles are stiff and don’t relax properly. When this happens, your ventricles don’t fill with blood as they should, and you may experience pressure buildup in your heart. This can progress to diastolic heart failure, resulting in fluid buildup in your lungs, abdomen and legs.
Results: Mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 47%, with 209 patients having an LVEF <50%. Invasive measurements showed elevated LV filling pressure in 58% of patients.
For patients with normal LV ejection fraction, normal LV filling pressure is present if E/e′ is less than 8. If septal E/e′ is 15 or more, lateral E/e′ is 12 or more, or average E/e′ is 13 or more, elevated LV filling pressure is present.Despite the presence of impaired left ventricular relaxation, the markedly elevated left atrial pressure results in a high velocity of early diastolic filling, which stops abruptly because of an abnormally rapid rise in ventricular pressure and atrial dysfunction.As LV filling pressure progressively elevate, the LAVI size will enlarge. Therefore, an enlarged LAVI is a marker of elevated LAP. In contrast, a small or normal LAVI is suggestive of normal LAP. The abnormal cut-off value for LAVI is > 34mL/m².

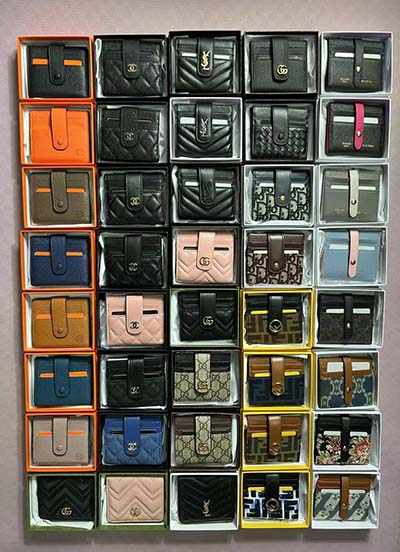
LV Heritage 35mm Reversible Belt. $1,090.00. Item Unavailable. LOUIS VUITTON Official Canada site - Discover our latest LV Heritage 35mm Reversible Belt, available exclusively on louisvuitton.com and in Louis Vuitton stores.
elevated lv filling pressure meaning|impaired Lv relaxation on echo